
Industrial networks have transformed automation. They allow machines and devices to talk to each other, boosting production speed, volume, and efficiency. But with this progress comes a hidden cost: complexity. One network glitch can bring the entire line to a halt, causing hours of lost output.
Figure 1. Industrial networks improve efficiency but increase troubleshooting challenges.
Globally, downtime costs industries an estimated $1.4 trillion per year. The number of downtime incidents has been decreasing since 2019, but the restoration time to fix issues is increasing by 65%. [2] Without strong troubleshooting practices, the time spent on fixing downtime-generating problems drags on, compounding losses. The good news? There are proven ways to prevent it.
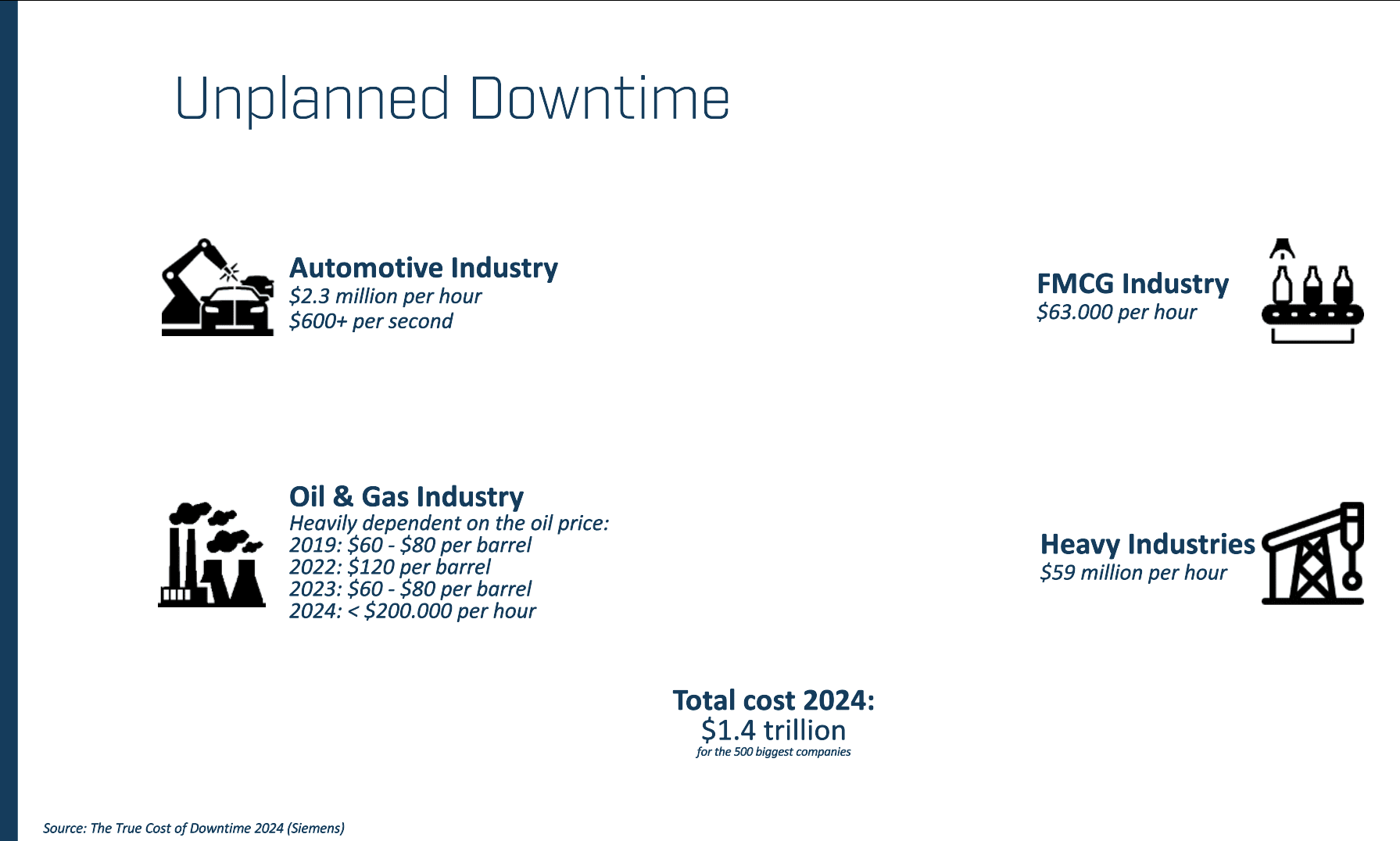
Graphic 2. Costs of dowtime per industry
References
¹ IndustryWeek, “Unlocking performance,” Emerson, accessed September 26, 2022.
² Siemens: The true cost of downtime 2024.
Downtime isn't inevitable. With the right mix of proactive maintenance, smart tools, and skilled people, companies can prevent problems before they happen—or resolve them quickly when they do. Here are a few proven strategies that significantly reduce downtime and keep production running smoothly.
Real-time monitoring tools give you constant visibility into your network. With customizable dashboards and alarms, you'll know about problems before they stop production. Engineers can act fast, either preventing downtime entirely or cutting its duration to a minimum.
Hardware failures happen and they're the number one cause of network communication issues. Stock essential spares like connectors, cables, and hubs. Skimping on quality parts may save upfront, but failures cost far more when the line is down.
Traditional troubleshooting demands years of expertise across multiple protocols. AI tools trained on industrial data can pinpoint root causes instantly. This reduces reliance on a handful of veteran field engineers and cuts both repair time and costs.
Even the best hardware and software fall short without skilled staff. Certified training gives engineers hands-on experience to design, install, maintain, and troubleshoot networks effectively. A trained team boosts uptime and ensures long-term resilience.
Cutting downtime isn't just about saving hours. It also:
On average, companies that adopt proactive maintenance reduce downtime to around 2 hours per month—a major improvement compared to the figures presented earlier.
When it comes to troubleshooting, the difference between a reactive and a proactive approach is dramatic.
With a reactive approach, problems are only addressed once production stops. Engineers must travel to the site, collect data, diagnose the issue, and implement a fix before operations can resume. If the fault is intermittent, it may not even appear during the inspection—forcing teams to wait for the problem to reoccur before it can be resolved. This not only prolongs downtime but also frustrates both staff and customers.
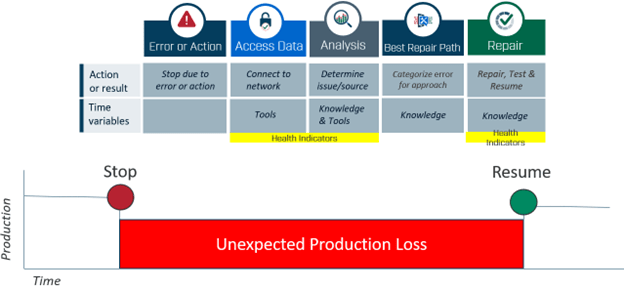
By contrast, a proactive approach with permanent monitoring removes blind spots. Real-time tools provide alerts for both critical and non-critical issues, giving companies the chance to plan maintenance activities in advance. This enables engineers to pinpoint and fix root causes quickly, avoiding unexpected shutdowns and keeping production on track.
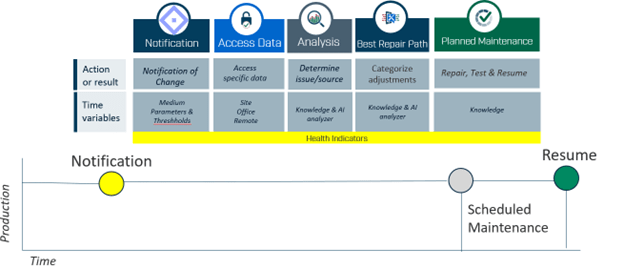
Minimizing downtime improves more than just productivity. Reduced interruptions also translate into:
In short, less downtime means not only greater efficiency but also a leaner, more sustainable operation.
Permanent monitoring also boosts workplace safety. With remote access to network data, engineers no longer need to enter unpleasant or hazardous environments just to check system status. This reduces risk, speeds up diagnostics, and frees teams to focus on higher-value tasks. The result: safer employees, smoother operations, and higher overall efficiency.
Meet the Atlas2 Plus: Anybus' next-gen OT network monitoring solution that keeps downtime from disrupting your business.
Designed for multi-protocol environments, the Atlas2 Plus delivers 24/7 visibility, predictive diagnostics, and intuitive visualizations that make even the most complex industrial networks easy to understand and manage.
By simplifying troubleshooting and empowering teams of all skill levels, it enables proactive maintenance and ensures reliable uptime across PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, and beyond.