
In this post, we deal with different bus topologies that are used in automation technology. The bus topology describes the way in which devices are connected to each other in a network. In industrial automation, a wide range of fieldbuses are used, which are also characterized by different topologies.
What topologies are distinguished and what characterizes them?
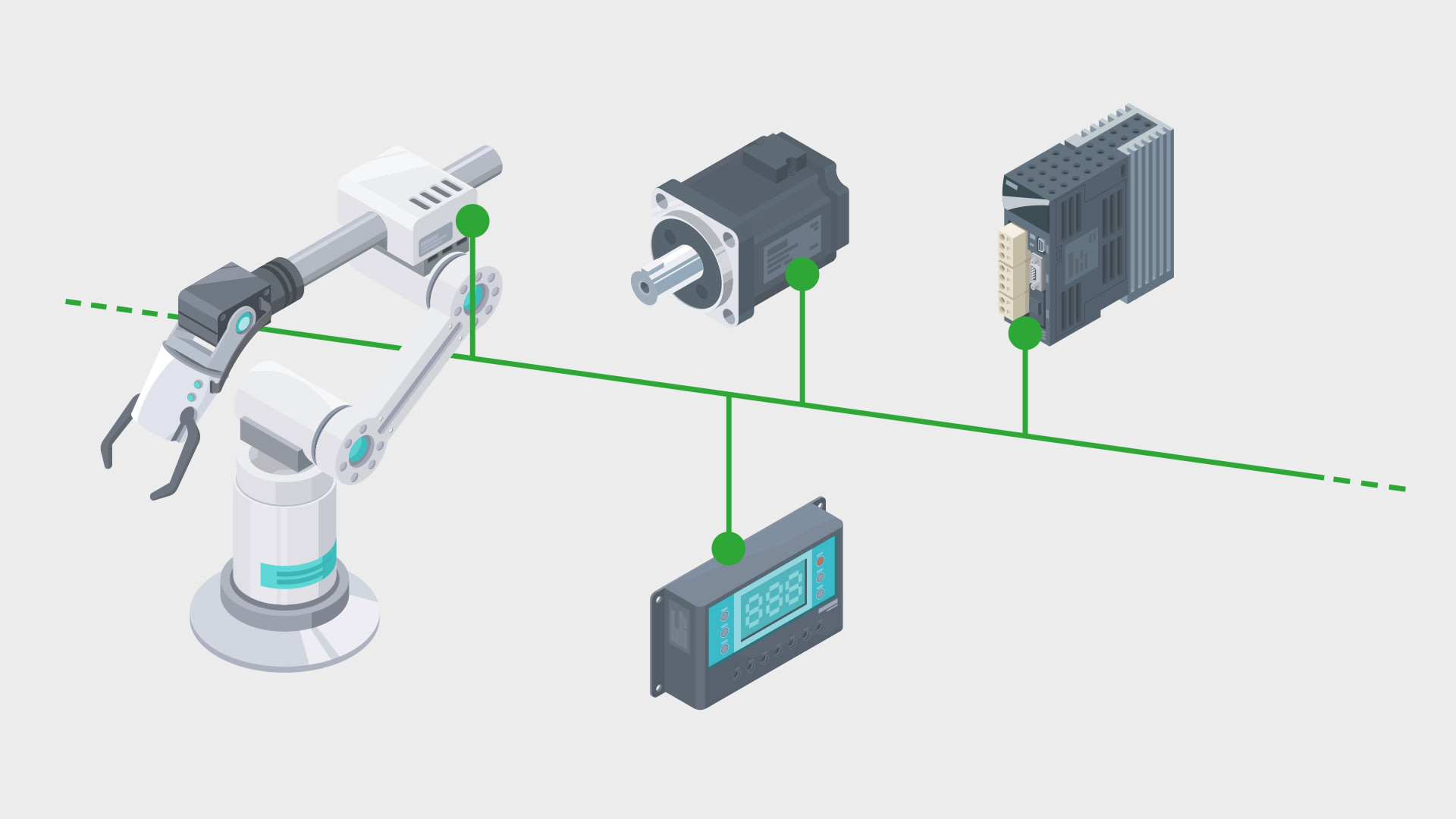
The line topology or bus topology is one of the simplest forms of network topologies. All devices are connected to each other in a linear sequence here. Every device is directly connected to a common line, the so-called bus. PROFIBUS is a good example of the application of this topology in industrial automation. It allows for efficient communication between control units and field devices.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
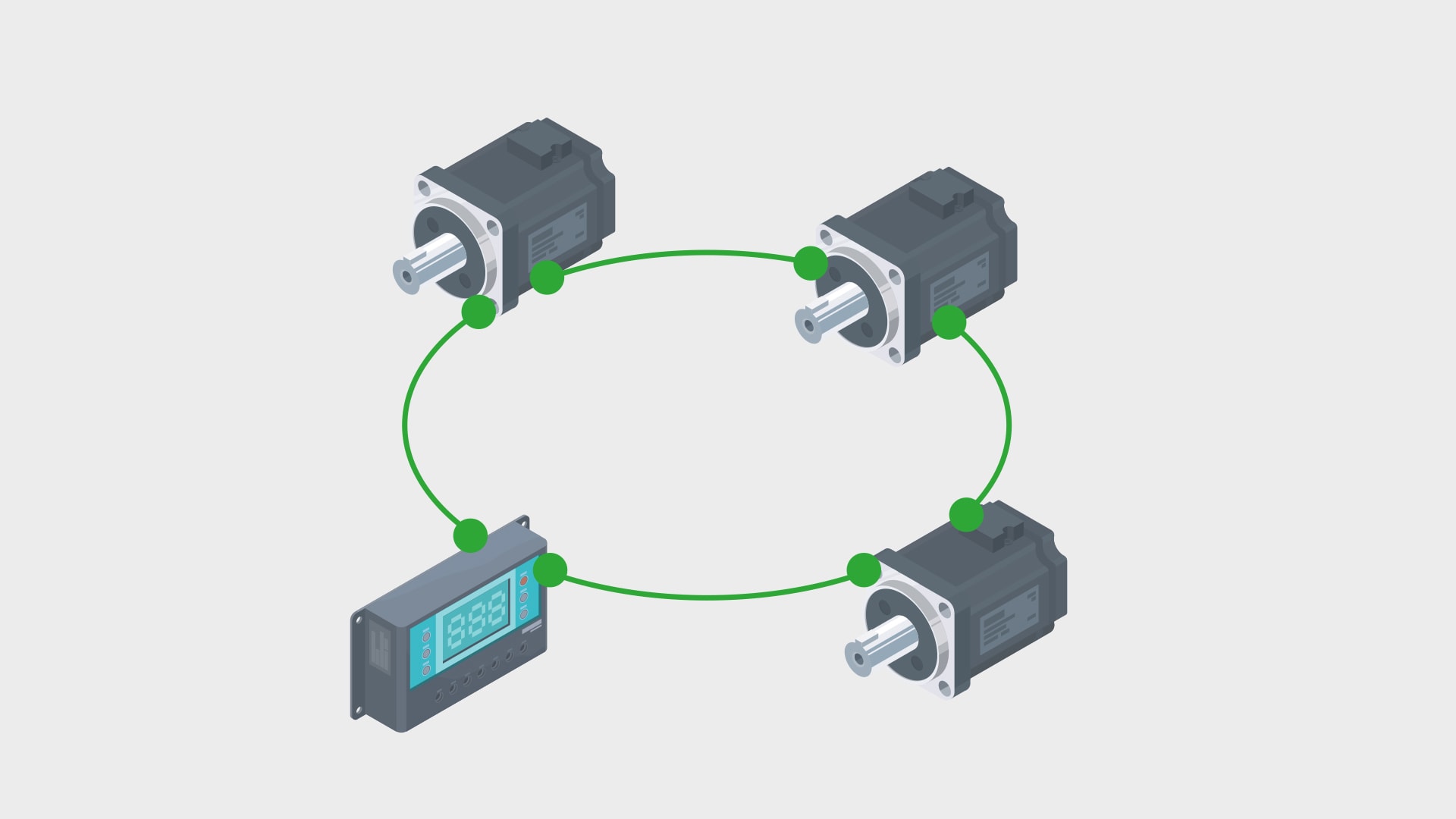
All devices are arranged in a closed circle in the ring topology. Each device has exactly two neighbors and communicates along the ring. Token ring, even though it is less widespread in modern networks, shows how this topology works.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
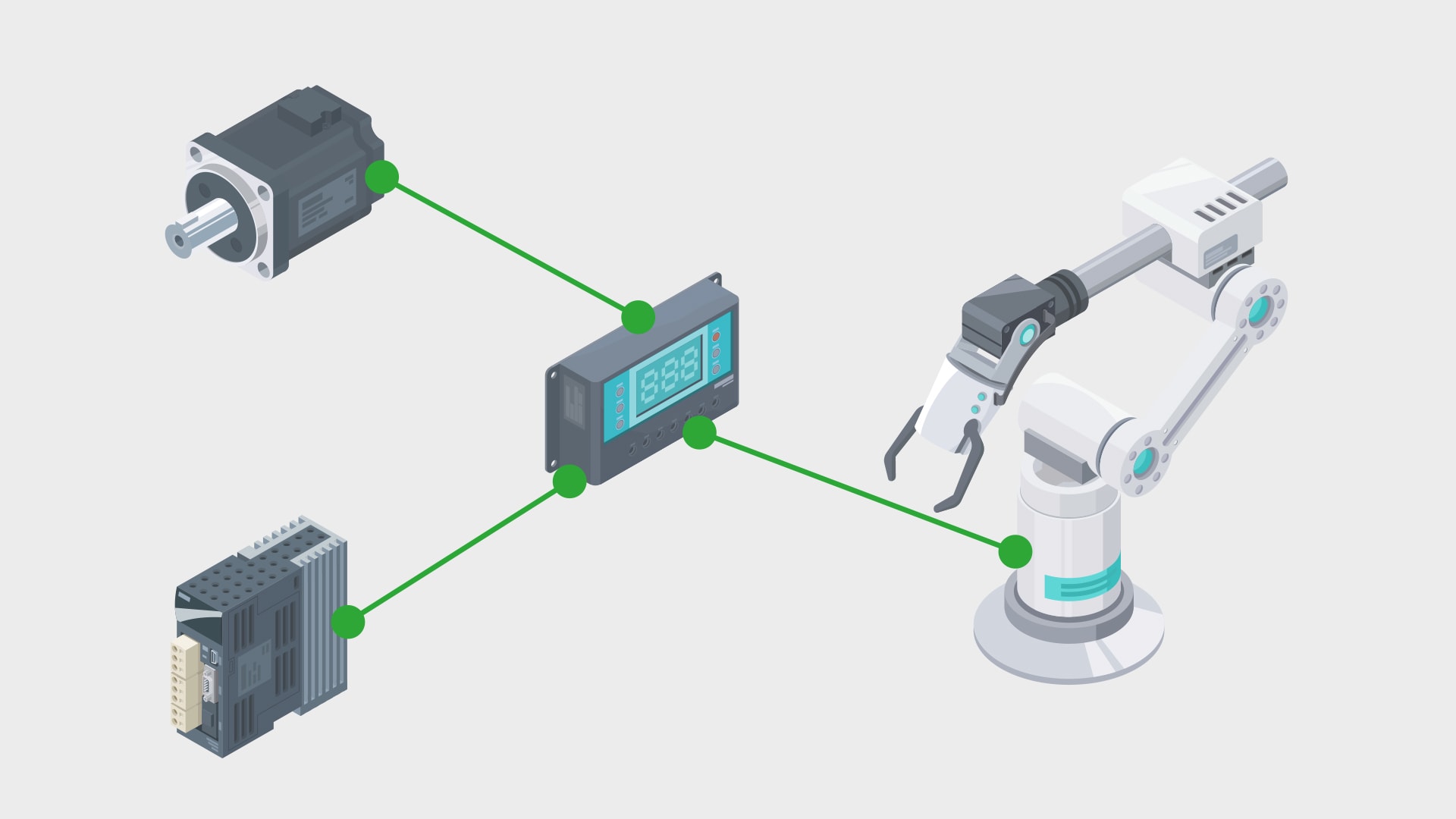
In the star topology, each device is connected to a central hub or switch. Data that is transmitted between devices always passes through this central node. Ethernet networks often use a star topology, which makes maintenance and scaling easier.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
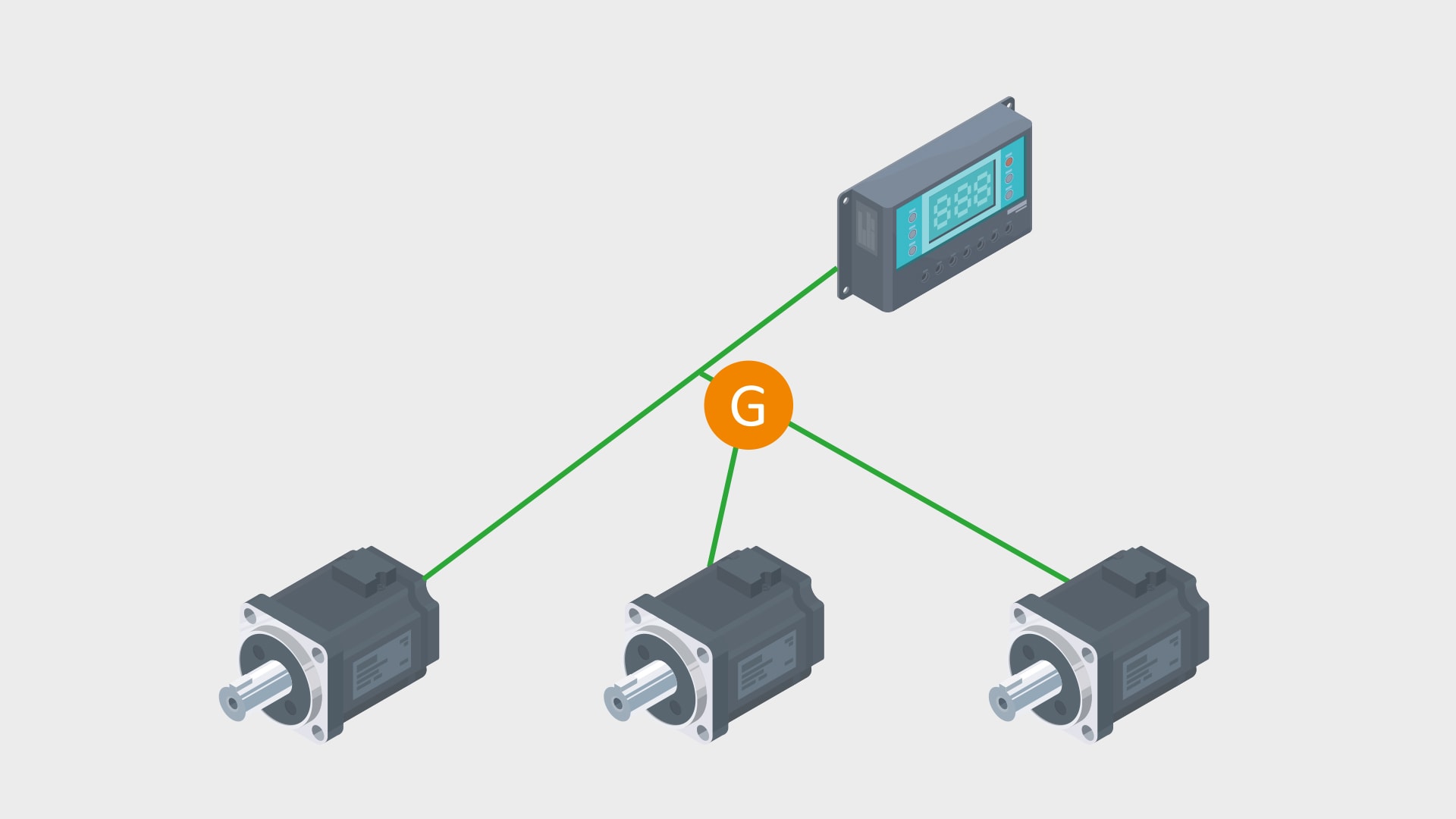
The tree topology, often also referred to as a hierarchical topology, is a mix of star and bus topologies. It consists of a central line (bus) to which several star networks are connected. Every star network acts like an independent branch of the tree.
Controller Area Network (CAN) is a good example of tree topology. At its core, CAN is based on a bus topology where all devices are connected to a central communication bus, which allows for an efficient and low-cost data transmission. CAN, however, can be expanded into a tree topology to increase range and flexibility. This is done by using bridges and repeaters, which make it possible to connect several bus segments to each other. This creates a more complex and more powerful network structure that meets the requirements of larger and more sophisticated systems, without sacrificing the fundamental advantages of the bus topology, such as simplicity and reliability.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Every topology offers its own unique advantages and challenges, from the simplicity and cost efficiency of the line topology, to the flexibility and expandability of the tree topology.
However, the selection of a specific fieldbus in automation technology can tie the user to the associated topology framework conditions. Every fieldbus has its own unique network structures, which significantly influence the system architecture.